Android Drawable
Success doesn’t come to you. You go to it. — Marva Collins

[TOC]
A Drawable is a general abstraction for “something that can be drawn.” Most
often you will deal with Drawable as the type of resource retrieved for
drawing things to the screen; the Drawable class provides a generic API for
dealing with an underlying visual resource that may take a variety of forms.
Unlike a {@link android.view.View}, a Drawable does not have any facility to
receive events or otherwise interact with the user.
Drawable 一般指可绘制事物的抽象,通常情况下, Drawable 作为控件的背景图像或者是简单的指示器(例如音量指示器),不像 View 一样能够处理时间传递,也就不能完成和用户交互的动作
一般的 Drawable
我们一般都可以通过 XML 来创建 Drawable 资源, 通过 Drawable Resources 来定义,可绘制对象资源是一般概念,是指可在屏幕上绘制的图形,以及可以使用 getDrawable(int) 等 API 检索或者应用到具有 android:drawable 和 android:icon 等属性的其他 XML 资源的图形。共有多种不同类型的可绘制对象
Drawable 动画
Drawable 动画,也就是常说的帧动画,通过按时间顺序播放一组图片来形成动画,通常在 res/drawable 下通过 xml 文件来创建:
实现动画对应的类是: AnimationDrawable,看继承关系:
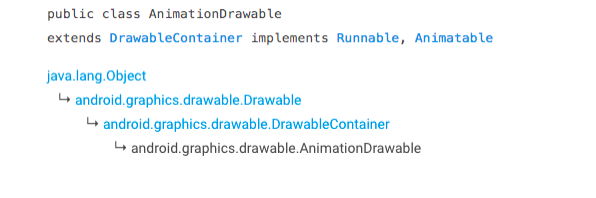
可见它通过实现 Animatable 接口来控制动画,这个接口是自定义 Drawable animation 时应该实现的,里面包含了三个方法,分别是开始、停止、判断是否在动画。
Drawable 是一个抽象类,我们可以通过继承它来绘制我们需要的 Drawable, 为了方便绘制,它还提供了一些通用的方法,例如:
- setBounds() 确定 Drawable 绘制区域
- getPadding() Drawable 的 padding, 该方法返回 false 代表没有设置 padding
- setState() 控制不同状态下的 drawable,如获得焦点时,按下时
- setLevel() 设置 drawable 的 lever 值
- 实现 Callback 接口, setCallback() 如果要实现 drawable 动画效果,必须实现该接口
自定义 Drawable 动画
我们通常做动画都是自定义 View 来实现,通过上面的 AnimationDrawable 来看,我们也可以通过自定义 Drawable 这种方式来实现动画,也算是利用代码绘制出帧动画这种效果,这种实现方式算是比较轻量级的,因为我们不用处理事件。
下面的项目算是比较经典的自定义 Drawable 动画了,通过工厂模式创建了一大批自定义加载动画,很酷炫,下面也将记录学习该开源库的笔记,同时结合另一个开源库学习。
继承 Drawable 来实现 Drawable 动画
继承 Drawable 需要复写下面几个方法,我们主要是通过 draw 方法来绘制特定的动画效果:
|
|
另外,我们还需要通过实现 Animatable 接口来控制动画开始、暂停,判断动画是否在进行:
|
|
此外,为了方便动画的重绘与调度,我们还需要给自定义的 Drawable 设置一个 Callback 接口 (Drawable 内部接口),此接口用来控制 Drawable 的重绘,以及下一帧动画的调度:
|
|
因为 Drawable 类里面的方法 invalidateSelf() 调用的就是 callback 里面的 invalidateDrawable() 方法
|
|
在 invalidateDrawable() 方法里面我们就可以来控制 Drawable 的重绘了。
- 通过这种方法实现的动画效果,我们就可以给控件添加 Drawable 动画,例如:
|
|
具体例子可看例一。
继承 View 来实现 Drawable 动画
Drawable 和 View 有点相似,比如都可以 draw ,绘制出特定的效果,但是 Drawable 比起 View 在这方面算是比较轻量级的,因为它不支持事件处理这块,通常我们自定义 View 动画可能很少考虑在 View 里面引用一个 Drawable 来通过它完成动画绘制,这种情况在自定义帧动画的时候可能比较有效,通过学习例二,也可以看到里面就是这么处理的,自定义一个 View(View类其实是实现了上面的 Callback 接口的), 完成测量、给 Drawable 设置绘制区域、绘制时调用 Drawable 的 draw 方法、重写 invalidateDrawable() 方法完成重绘制、也可以接受事件处理等。
写动画效果,实现方式很多,感觉最重要的就是分解动画效果,理清楚动画的绘制流程,在具体绘制的时候学会灵活实现。比如说画一个圆,不停的缩放形成动画,我们可以不断改变半径重新绘制,也可以跟简单的直接对画布进行缩放。无论多么复杂的动画,都是有简单的动画组合起来的,先分解,在组合。
在 AVLoadingIndicatorView 中,是一个很好的自定义 Drawable 动画的例子,AVLoadingIndicatorView 是一个继承 View 的自定义 View ,主要完成的工作是控件大小的测量,以及控制动画的开始以及结束等,而最重要的具体绘制则是由自定义的 Indicator (自定义 Drawable 工厂类) Drawable 继承类来实现的,也就是绘制实际是 drawable 自己来完成的。理一下过程:
- 工厂 Indicator 继承自 Drawable 实现 Animatable 接口
- 抽象方法 创建动画 和 具体绘制过程 延迟到子类 去实现具体细节
- Indicator 中 onBoundsChange() 方法接受 AVLoadingIndicatorView 中测量出来的大小,来决定 drawable 的绘制区域
- Indicator 中重绘方法 invalidateSelf(), 会回调到 Drawable.Callback 接口中的 invalidateDrawable() 方法,在这里控制重绘逻辑
- AVLoadingIndicatorView 继承 View,而 View 是实现了 Drawable.Callback 的,所以我们只需重写接口中的方法invalidateDrawable() 来控制重绘流程, 之后调用 View 的 invalidate(), 再到 onDraw() 控制绘制,最后将绘制任务再传到 Indicator 中的 draw() 方法,这就是整个绘制流程。
- 记得给 Indicator 注册 Callback 接口,学会控制 scheduleDrawable() 与 unscheduleDrawable()
- 值得注意 重写 verifyDrawable() 方法,如果我们自定义的 View 展示自己的 Drawable 动画的时候,看下面的源码:1234567891011121314151617181920212223242526/*** If your view subclass is displaying its own Drawable objects, it should* override this function and return true for any Drawable it is* displaying. This allows animations for those drawables to be* scheduled.** <p>Be sure to call through to the super class when overriding this* function.** @param who The Drawable to verify. Return true if it is one you are* displaying, else return the result of calling through to the* super class.** @return boolean If true than the Drawable is being displayed in the* view; else false and it is not allowed to animate.** @see #unscheduleDrawable(android.graphics.drawable.Drawable)* @see #drawableStateChanged()*/protected boolean verifyDrawable(@NonNull Drawable who) {// Avoid verifying the scroll bar drawable so that we don't end up in// an invalidation loop. This effectively prevents the scroll bar// drawable from triggering invalidations and scheduling runnables.return who == mBackground || (mForegroundInfo != null && mForegroundInfo.mDrawable == who);}
上面就是一些自定义 Drawable 的动画的总结了,也算是记录下如何用 Drawable 来实现动画,在项目中我们可能直接上自定义 View 来做动画了,AVLoadingIndicatorView 也可以直接自定义自 View,绘制的时候也就不用绕到 drawable 里面了,但在一些情况中感觉使用 Drawable 动画显然更好一些,比如无需交互的帧动画,加载动画,如 Fresco 中自定义的图片加载动画也是要通过 Drawable 来做。